Unicast, multicast and broadcast are the three simple methods used to transmit packets over a network. However, do you really have a good understanding of these networking terms? Here focus on unicast vs multicast vs broadcast to tell you their differences.
What Is Unicast?
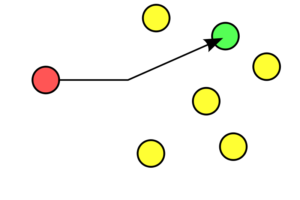
Unicast is defined as the connection that only between a server and a client, which means it’s a one to one transmission. In computing world, it’s the most common kind of traffic in TCP/IP networks. For example, when you send or receive the email, you have to connect to the email server. And here you use the unicast transmission. In this case, a unicast frame contains the unique unicast MAC address of the destination receiver. Therefore, only the specified destination can receive the unicast traffic, and all other destinations will ignore or can’t receive unicast traffic. Using this transfer method, the server can send personalized and accurate information to each client with different requests. However, when the same information needs to be sent to a large audience, multicast and broadcast methods will be more efficient.
Figure 1: Example of Unicast One to One transmission
What Is Multicast?
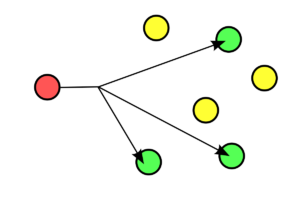
Multicast is a one to many technology that efficiently sends data from one source to many destinations simultaneously, generally within a Local Area Network. A multicast frame contains the unique multicast MAC address of an application, protocol or data stream. To implement IP multicast communication, equipment like data switch, router between the source and receivers is required to support IP multicast function. In multicast model, the network traffic will not increase since the data packet can be sent to different destinations of one multicast group by sending one copy of the data, which means the overall network load can be reduced. However, as we mentioned above, the operation of multicast requires the assistance of switches with IP multicast function, so no matter you choose a 10gb ethernet switch or Gigabit PoE switch, please make sure the switch has that function.
Figure 2: Example of Multicast One to Many Transmission
What Is Broadcast?
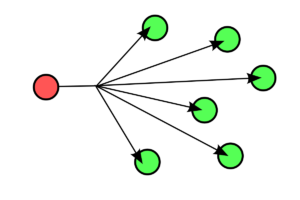
Broadcast is a one to all technology. When a device sends a packet to the broadcast MAC address (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF), it will be delivered to all receivers that connected on the LAN no matter the receiver needs it or not. Cable television network is the typical broadcast network example. However, broadcast is not the suitable choice for the public Internet, because it will generate unnecessary interference and tons of unwanted data.
Figure 3: Example of Broadcast One to All Transmission
Unicast vs Multicast vs Broadcast: What Are the Differences?
After knowing the definitions of unicast, multicast and broadcast, we’ll make a comparison of unicast vs multicast vs broadcast.
Multicast vs Unicast
The basic difference is that, in unicast, there is only one sender and one receiver, while there is a single sender but multiple receivers in multicast. When we want to send the message to a number of people, we’d better choose multicast transmission since it can utilize the bandwidth more efficiently.
Multicast vs Broadcast
In broadcast, the packet transmission is one to all, but in multicast the transmission is one to many. Besides, multicast requires group management, in order to ensure the message can be sent to those hosts which are interested in receiving the message. And the traffic on the multicast network is under control.
Unicast vs Broadcast
The process of data transmission is different. Unicast only sends the data to one receiver, but broadcast sends the same data to all receivers connected in one LAN. Moreover, if you want to share some private or unique information with another person, you must use unicast network but not the broadcast.
Here is a table to give you a clear comparison of unicast vs multicast vs broadcast.
| Unicast | Multicast | Broadcast | |
| Transmission |
One to one
| One to many |
One to all
|
Bandwidth
|
Wasted
|
Utilized efficiently
|
Wasted
|
Group management
|
No
|
Yes
|
No
|
Security
|
Safest
|
Safe
|
Not safe
|
From the table, we can see that multicast is the most efficient method for data transmitting. To meet the market demand, almost all FS network switches have multicast function.
Conclusion
As regard with unicast vs multicast vs broadcast, we know the key difference between them is the different transmission paths. So when you need to transmit some information, choose the suitable transmission method based on your actual needs.